Page 3 - CHARACTERIZATION OF THE C-2W PLASMA GUNS
P. 3
Nucl. Fusion 57 (2017) 116021 H. Gota et al (a)
(b)
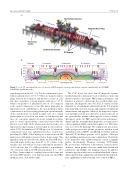
Figure 1. (a) C-2U experimental device; (b) sketch of FRC magnetic topology and density contours, simulated by the 2D MHD LamyRidge equilibrium code.
typical magnetic eld is Bz ~ 0.1 T in the con nement region with an end-mirror ratio of 3.0–3.5. There are magnetic mirror plugs between the formation and divertor sections at each side that can produce a strong magnetic eld up to ~1.5 T, which corresponds to a plug-mirror ratio of ~15 compared to the central con nement section. The mirror plugs play an important role in contributing to the open- eld-line plasma con nement as well as assisting plasma-gun operation inside of the end divertors. As shown in gure 1(b), two coaxial plasma guns are located on axis inside of each divertor, and there are concentric annular electrodes behind the plasma guns to control open- eld-line connection/contact with the divertor vessel walls. Both, plasma guns and electrodes, are important for edge biasing as well as radial electric eld con- trol in C-2U. Six brand new C-2U NB injectors, located in the con nement vessel, were substituted for those used in C-2, providing 10+ MW (15 keV hydrogen) of increased total NB input power with higher current at lower beam energy. The upgraded setup also provides the ability for tilted NB injec- tion with angles in the range from 65° to 75° relative to the machine axis and with an average radial impact parameter of 0.19 m; note that C-2’s NB system had a perpendicular (90°) injection setup in the NB-injection planes at z = ±0.5 m. These features improve coupling between the beams and the target FRC plasma, even under pronounced axial FRC shrinkage after a few milliseconds.
The C-2U device has more than 60 diagnostic systems installed along the con nement vessel, formation sections, and divertor regions to investigate FRC plasma performance and behavior as well as to characterize the overall machine oper- ating state. The diagnostic suite of C-2U [13] consists of a fun- damental set of instruments inherited from the C-2 program [14] along with a few new systems and a number of signi cant enhancements and upgrades. Much of the diagnostics expan- sion and improvements were driven by an increased focus on the open- eld-line plasma, which appears to have consider- able impact on the core FRC and overall system performance. Signals and data from individual diagnostics are transferred to a data-acquisition (DAQ) system that acquires over 1000 chan- nels on every C-2U discharge. The acquired raw data is gen- erally post-processed into plasma parameters and then stored on databases such as MDS+ and MySQL for further analysis. Typical C-2U discharges generate over 1 gigabyte of data per shot, including analysis movies and computations. Overall, the C-2U diagnostics suite includes magnetic sensors, Langmuir probes, interferometry, Thomson scattering, VUV/visible/ IR spectroscopy, bolometry, re ectometry, neutral particle analyzers, fusion product detectors, multi-chord far-infrared polarimetry, and multiple fast imaging cameras. In addition, extensive ongoing work focuses on advanced methods of meas- uring separatrix shape and plasma current pro le that will facil- itate equilibrium reconstruction and active control of FRCs.
3